OU’s Interprofessional Education Workshop teaches students about palliative and end-of-life care

More than 350 people participated in Oakland University’s seventh annual Interprofessional Education (IPE) Workshop, an event that brings together students, faculty and community leaders from various health care disciplines with the goal of improving care for patients and their families.
This year’s event focused on therapeutic communication in palliative care and at end of life. The Center to Advance Palliative Care defines palliative care as specialized medical care for people living with a serious illness. This type of care is intended to alleviate the symptoms and stress of illness for patients and families and is available to all populations from newborns to elderly individuals. It can be offered as part of end-of-life care or for those who are seeking curative treatment. IPE Workshop organizers chose the topic of therapeutic communication in palliative care and at end of life to introduce students to an area of health care that affects nearly all people at some point in their lives.
“The Interprofessional Education Workshop uses experiential learning to increase students’ awareness of leading health issues and the importance of interprofessional collaboration to address them,” said Caress Dean, associate professor and chair of OU’s Interprofessional Education Task Force. “This year’s workshop was specifically designed to help students deal with the unique challenges of caring for patients who are facing severe and even terminal illnesses. There can be a lot of fear and discomfort around these issues – for patients, families and health care professionals themselves – which is why it’s important to have these interprofessional discussions and learning opportunities.”

Toni Glover, keynote speaker at this year's IPE Workshop
Participants learned about the development and practice of palliative care, as well as how to communicate effectively with patients, families and interprofessional team members. This year’s event was keynoted by Toni Glover, associate professor and Ascension Providence Rochester Endowed Professor in Oakland University’s School of Nursing. Glover shared her expertise as a researcher, educator and geriatric nurse practitioner with a focus on helping current and future health professionals strengthen their therapeutic communication skills.
“When you’re in school, you’re really focused on the mechanical skills of starting an IV or putting in a Foley catheter, but I truly believe that learning how to communicate effectively will improve all of your care with patients and will help you to develop a therapeutic relationship that can help patients achieve their goals,” she said. “Communication is not an innate ability, it’s something you can learn and refine.”
Glover noted that palliative care is a relatively new area of specialization in health care. The demand for palliative care services continues to grow, with not enough specialists trained to provide them. The Lancet Commission on Global Access to Palliative Care and Pain Relief found that there are 61 million people who could benefit from palliative care who are not receiving it.
“To meet the vast need for palliative care, we need all health care professionals to have some primary palliative care skills and that’s why developing your communication skills in this area is so important,” said Glover.
Primary palliative care skills include helping patients and families identify goals of care, communicating illness treatment options and prognosis information, performing a pain and symptom assessment, helping patients and families with social and spiritual needs, and addressing cultural issues. Glover shared three strategies to enhance therapeutic communication with patients and families:
- Patient Dignity Question – What do I need to know about the patient to give them the best possible care?
- Ask-Tell-Ask Method – a strategy for conveying information and assessing patient understanding of their condition
- N.U.R.S.E. (Name, Understand, Respect, Support, Explore) Acronym – tool for responding to patient emotions.
“Therapeutic communication is a tool for the health professional to use with patients and families to enhance patients’ sense of safety trust, health and well-being,” Glover said. “That is really what we are aiming for as health professionals is to have a therapeutic interaction with those we are serving.”
Following the keynote address, students gathered in small interprofessional groups to discuss a case study of a patient dealing with a serious health condition. Group members represented a broad range of health care professions, including nursing, physical therapy, medicine, public health and social work. Each group was led by a faculty facilitator and a student facilitator who helped guide discussion on how members of an interprofessional team can work together to serve the physical, psychological, social and spiritual care needs of patients and their families.
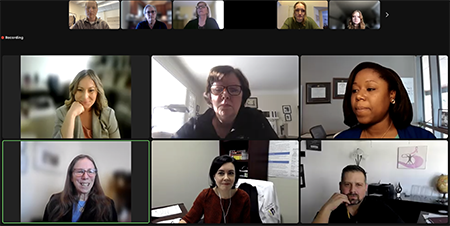
Panel discussion participants, top row from left: Maria Beam, Stephanie Brandimarte and Caress Dean. Bottom row, from left: Olga Ehrlich, Stacey Ruff and Christopher Wilson

 February 13, 2023
February 13, 2023